May 6
/
Skillmed Institute
Understanding and Managing: Thyroid-Related Hair Loss
This butterfly-shaped gland in the neck produces two vital hormones, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). The primary function of this gland is to control metabolic rate. Hence, it influences the working of most major organs like the heart, digestive system, brain health, and bone mineral density.
Adverse Changes in Metabolism Causes Hair Loss:
Human hair grows slowly, passing through different growth phases, with each cycle lasting for a few years. If this cycle is accelerated, hair might start falling faster. On the other hand, if this cycle slows down, hair growth will be affected. Therefore, both the acceleration and slowdown of metabolism will negatively impact hair health.
This means that hair loss may occur both due to hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Studies suggest that about 50% with hyperthyroidism will experience hair loss, and about 33% with hypothyroidism will experience hair loss. So, healthcare professionals need to know that there is a significant association between thyroid function and hair health.
Thyroid diseases are often secondary to nutritional deficiencies (iodine deficiency in hypothyroidism), chronic diseases, inflammation, and auto-immune disorders (like Graves' disease or Hashimoto's disease). These issues also contribute to hair loss in those living with thyroid problems.
Managing Thyroid-Related Hair Loss:
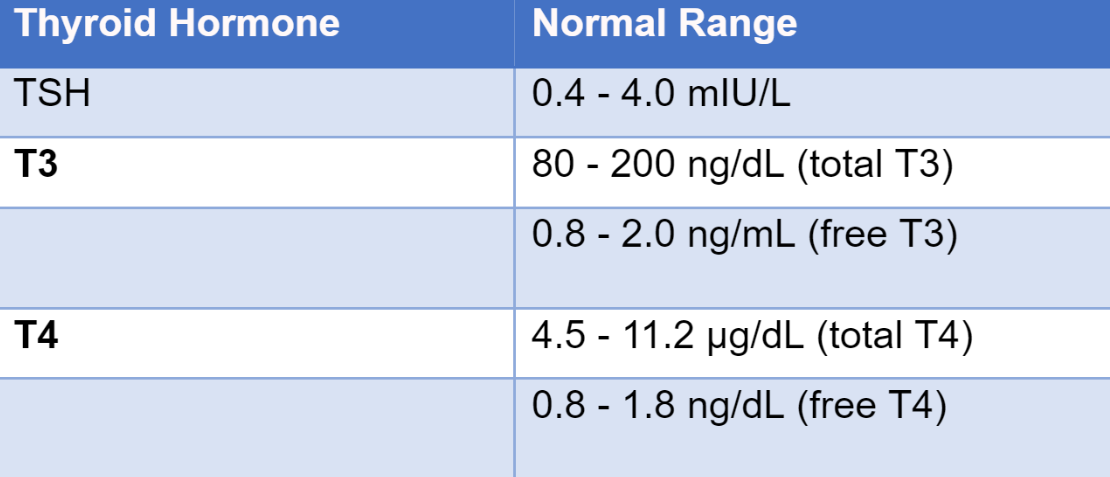
To understand what treatment approach will work for thyroid-related hair loss, it is vital to understand whether the person is living with hypothyroid or hyperthyroid. Although symptoms can help diagnose the issues, it may be challenging in mild cases. Hence, it is vital to go for a thyroid panel blood test, which includes testing for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) levels.
The next step is treating the underlying problem causing thyroid issues. This may mean managing inflammation, auto-immune disorders, and more.
Apart from managing thyroid issues, it is vital to stimulate hair growth through non-pharmacological means.
Finally, it is good to know that hair loss caused by thyroid issues is reversible. However, hair growth may become visible only after a few months of initiating the treatment of underlying causes.
Hormone replacement therapy using levothyroxine is a golden standard for managing hypothyroidism.
Managing hyperthyroidism is a bit more challenging due to its diverse nature. Its treatment may include using medications like methimazole or propylthiouracil that suppress hyperthyroid. Some patients may need specific treatments like radioactive iodine or even surgery.
Apart from managing thyroid issues, it is vital to stimulate hair growth through non-pharmacological means.
The first thing to focus on is nutrition therapy. Certain nutrients that boost hair growth include a diet high in lean protein and omega-3 fatty acids.
Other dietary measures include increasing the intake of fruits, vegetables, and seeds. Seeds are especially rich in minerals and essential fatty acids.
Supplementing diet with zinc, selenium, and biotin may help. Biotin is among the few vitamins proven to help with hair loss.
Next, the treatment focus must be enhancing physical health and stress management. Enhancing overall health can boost hair growth and increase blood flow to the scalp. Similarly, stress management through exercise, yoga, and meditation may help.
Gentle hair care is another vital component of preventing hair loss. Avoid recommending excessive chemical treatments and harsh shampoos. Instead, consider a mild scalp massage.
Topical minoxidil may be considered for thyroid-related hair loss. However, it is worth understanding that evidence supporting its use in the condition is limited.
5-alpha reductase inhibitors like finasteride and dutasteride have no role in managing the condition and will only benefit patients if the patient is also experiencing androgenic alopecia concurrently.
Finally, it is good to know that hair loss caused by thyroid issues is reversible. However, hair growth may become visible only after a few months of initiating the treatment of underlying causes.

Company
Need Help?
Recruitment
Made in Europe ©2024 Skillmed

