Fighting Scalp Infections: Effective Treatment Strategies
Aug 26
/
Skillmed Institute
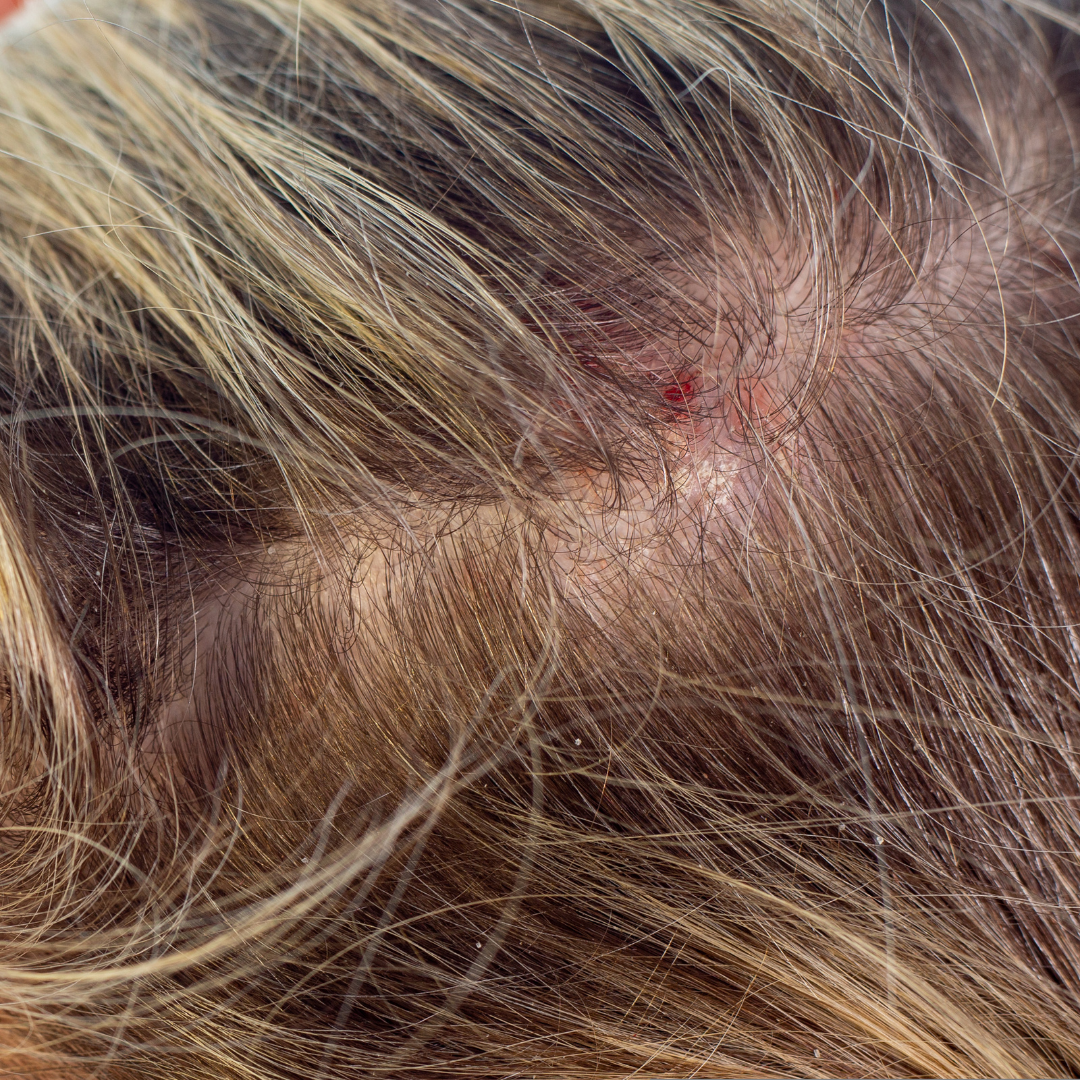
Scalp infections are a common dermatological concern. They not only cause discomfort, but may also lead to hair loss. These infections can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, making accurate diagnosis and treatment essential for maintaining scalp health.
Understanding Scalp Infections
Scalp infections can have varying presentation, depending on the underlying pathogen. Common bacterial infections include folliculitis, impetigo, and cellulitis, often caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus species.
Fungal infections, such as tinea capitis, are primarily caused by dermatophytes like Trichophyton and Microsporum species.
Additionally, viral infections, including herpes simplex, can affect the scalp, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective medical solutions for scalp infections. Clinicians should perform a thorough physical examination and consider laboratory tests such as KOH preparation for fungal elements, bacterial cultures, and PCR for viral pathogens.
Early identification of the causative agent allows for the selection of targeted effective scalp treatments.
Fungal infections, such as tinea capitis, are primarily caused by dermatophytes like Trichophyton and Microsporum species.
Additionally, viral infections, including herpes simplex, can affect the scalp, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective medical solutions for scalp infections. Clinicians should perform a thorough physical examination and consider laboratory tests such as KOH preparation for fungal elements, bacterial cultures, and PCR for viral pathogens.
Early identification of the causative agent allows for the selection of targeted effective scalp treatments.
Treatment Approaches
1. Antibacterial Therapy:
Topical Antibiotics: Mild bacterial infections such as folliculitis may respond well to topical antibiotics like mupirocin or clindamycin. These agents are effective against common pathogens and have a low risk of systemic side effects.
Systemic Antibiotics: For more severe infections like cellulitis or impetigo, systemic antibiotics are required. Cephalexin or clindamycin are often prescribed based on the susceptibility of the isolated pathogen.
2. Antifungal Therapy:
Topical Antifungals: Tinea capitis and other superficial fungal infections can often be managed with topical antifungal agents like ketoconazole or terbinafine. These agents disrupt the fungal cell membrane, leading to cell death.
Oral Antifungals: In cases of extensive infection or involvement of hair follicles, oral antifungals such as griseofulvin or terbinafine are indicated. These agents have been shown to be highly effective in eradicating fungal infections, though monitoring for side effects is necessary.
3. Antiviral Therapy:
For viral infections like herpes simplex, oral antiviral agents such as acyclovir or valacyclovir are the treatment of choice. These medications inhibit viral replication and can significantly reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
4. Supportive Care:
Maintaining scalp health during treatment is critical. Patients should be advised on proper hair care solutions, including gentle cleansing and avoiding irritants that could exacerbate inflammation or infection.
Scalp hygiene plays a pivotal role in preventing recurrent infections. Regular washing with medicated shampoos and maintaining short hair may reduce the risk of pathogen colonization.
Table 1. Treatment approaches to scalp infections
Topical Antibiotics: Mild bacterial infections such as folliculitis may respond well to topical antibiotics like mupirocin or clindamycin. These agents are effective against common pathogens and have a low risk of systemic side effects.
Systemic Antibiotics: For more severe infections like cellulitis or impetigo, systemic antibiotics are required. Cephalexin or clindamycin are often prescribed based on the susceptibility of the isolated pathogen.
2. Antifungal Therapy:
Topical Antifungals: Tinea capitis and other superficial fungal infections can often be managed with topical antifungal agents like ketoconazole or terbinafine. These agents disrupt the fungal cell membrane, leading to cell death.
Oral Antifungals: In cases of extensive infection or involvement of hair follicles, oral antifungals such as griseofulvin or terbinafine are indicated. These agents have been shown to be highly effective in eradicating fungal infections, though monitoring for side effects is necessary.
3. Antiviral Therapy:
For viral infections like herpes simplex, oral antiviral agents such as acyclovir or valacyclovir are the treatment of choice. These medications inhibit viral replication and can significantly reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
4. Supportive Care:
Maintaining scalp health during treatment is critical. Patients should be advised on proper hair care solutions, including gentle cleansing and avoiding irritants that could exacerbate inflammation or infection.
Scalp hygiene plays a pivotal role in preventing recurrent infections. Regular washing with medicated shampoos and maintaining short hair may reduce the risk of pathogen colonization.
Table 1. Treatment approaches to scalp infections
| Pathogen Type | Common Condition | First-line Treatment |
| Bacterial | Folliculitis | Topical Mupirocin |
| Bacterial | Cellulitis | Oral Cephalexin |
| Fungal | Tinea Capitis | Oral Terbinafine |
| Viral | Herpes Simplex | Oral Acyclovir |
Conclusion
Effective management of scalp infections requires an accurate diagnosis followed by targeted medical solutions scalp therapy. Combining effective scalp treatments with proper hair care solutions enhances outcomes and promotes long-term scalp health.

Company
Need Help?
Recruitment
Made in Europe ©2024 Skillmed

